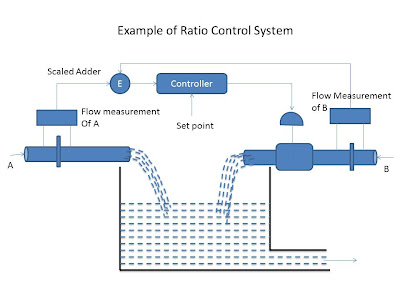
In this figure the ratio control system consists of the flow transmitter which senses the flow rate of the first pipe and second flow control. The flow controller controls the flow of the second pipe with respect to the flow in the first pipe.
Example of ratio control system
A common example is when the ratio of two reactants must be controlled is shown in the figure. One of the flow rates is measured but allowed to float, that is , not regulated. The outer flow rate is both measured and adjusted. The outer flow rate is both measured and adjusted to provide the specified control ratio. The flow rate of reactant A is measured and added with appropriate scaling, to the measurement of flow rate B. the controller reacts to the resulting input signal by adjustment of the control valve in the reactant B input line.
Application of ratio control system:
Blending operations
For holding the fuel-air ratio of reactants of the optimum.
Maintaining a stoichiometric ratio of reactance of a reactor.
Keeping a specified reflux ratio for a distillation column etc.